Planting Zones by ZipCode
What Planting Zone am i in?
To know the Planting zone you are in just enter your 5-digit zipcode.
Select your State from list below to view its detailed Planting Zone Map
Planting Zone Map
Zone Map
What are USDA Plant Hardiness Zones?
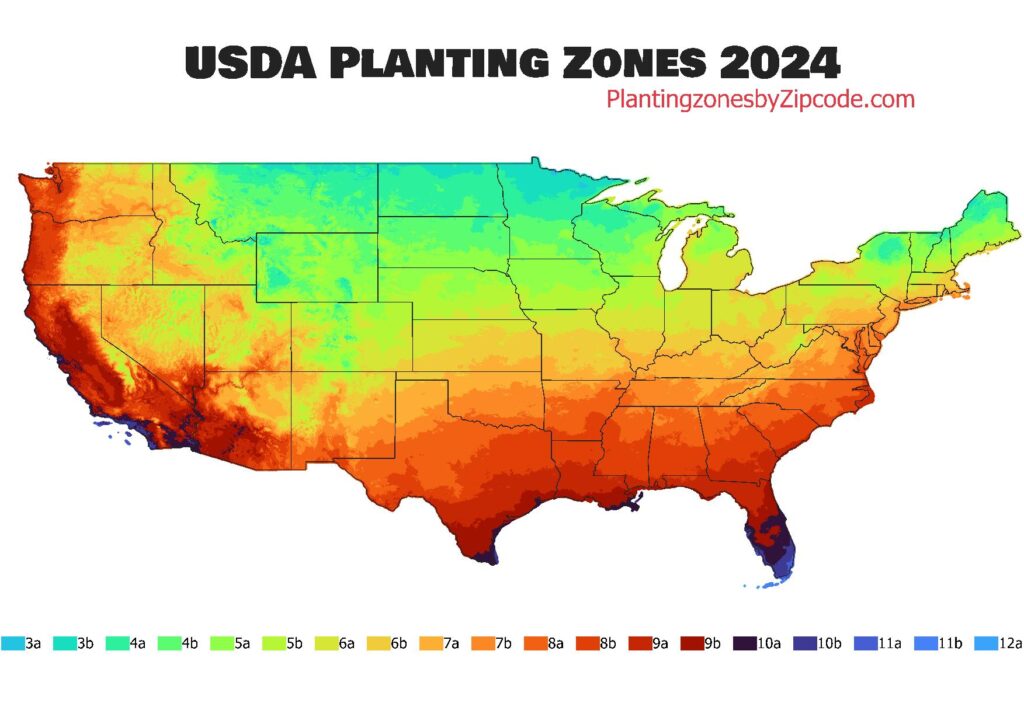
Planting zones, officially known as USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, are geographic regions categorized by their average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures. These zones help gardeners and growers select plants that are likely to survive and thrive in their specific climate. The USDA divides the United States into 13 distinct Planting zones, each representing a 10°F (5.6°C) temperature range. This classification system act as an essential guidance for plant selection and cultivation, ensuring that chosen plant species can withstand the typical winter conditions of a given area.
What are USDA Plant Hardiness Zones in 2024?
As of 2024 , the latest USDA Planting Zones data was released In November 2023. In this update the USDA released its updated Plant Hardiness Zones Map. This new version incorporates data from 13,412 weather stations, a significant increase from the 7,983 used in the 2012 map. The 2023 map is now considered the most accurate and detailed version to date, offering improved resolution and more precise zone classifications.
How are Plant Hardiness Zones Determined?
Plant Hardiness Zones are generated by analyzing the average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures across different regions of USA. After analyzing data USDA divides the United States into 13 distinct zones, each covering a 10°F (5.6°C) temperature range. These zones are further split into “a” and “b” half-zones, representing 5°F (2.8°C) increments.
For eg:
- Zone 6a: -10°F to -5°F (-23.3°C to -20.6°C)
- Zone 6b: -5°F to 0°F (-20.6°C to -17.8°C)
The 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map utilizes data from 13,412 weather stations, incorporating 30-year temperature averages from 1991 to 2020. This extensive dataset aims for an accurate and up-to-date representation of climate patterns across the country.
What Are the Differences Between Planting Zones?
USDA Hardiness Zones are distinguished by their average annual minimum winter temperatures, with each zone representing a 10°F (5.6°C) range. The concise difference is temperature range:
- Zones 1-4: Extremely cold (-50°F to -20°F / -45.6°C to -28.9°C)
- Zones 5-7: Cold to cool (-20°F to 10°F / -28.9°C to -12.2°C)
- Zones 8-10: Mild to warm (10°F to 40°F / -12.2°C to 4.4°C)
- Zones 11-13: Hot (40°F and above / 4.4°C and above)
Plant suitability varies significantly across these zones. For example:
- Zone 4: Cold-hardy plants like hostas, daylilies, and peonies
- Zone 8: Warmer climate plants such as azaleas, camellias, and magnolias
What Does My Planting Zone Mean for My Garden?
Your planting zone is a crucial guide for selecting perennial plants which are best suited to your local climate. It indicates the coldest temperatures that plants can reliably survive in your area. Here’s what your planting zone means for your garden:
- Perennial plant selection: Choose perennials, trees, and shrubs labeled for your zone or colder to ensure winter survival.
- Annual plants: Hardiness zones are less critical for annuals and vegetables grown in a single season.
Also, you should keep in mind microclimates. Your garden may have warmer or cooler spots due to other factors like:
- Proximity to buildings
- Wind exposure
- Shade levels
These microclimates can create a localized growing conditions that may differ from your overall zone classification, allowing for some flexibility in your plant choices. Understanding your planting zone and microclimates helps you optimize plant selection and placement, increasing the chances of a thriving garden.
